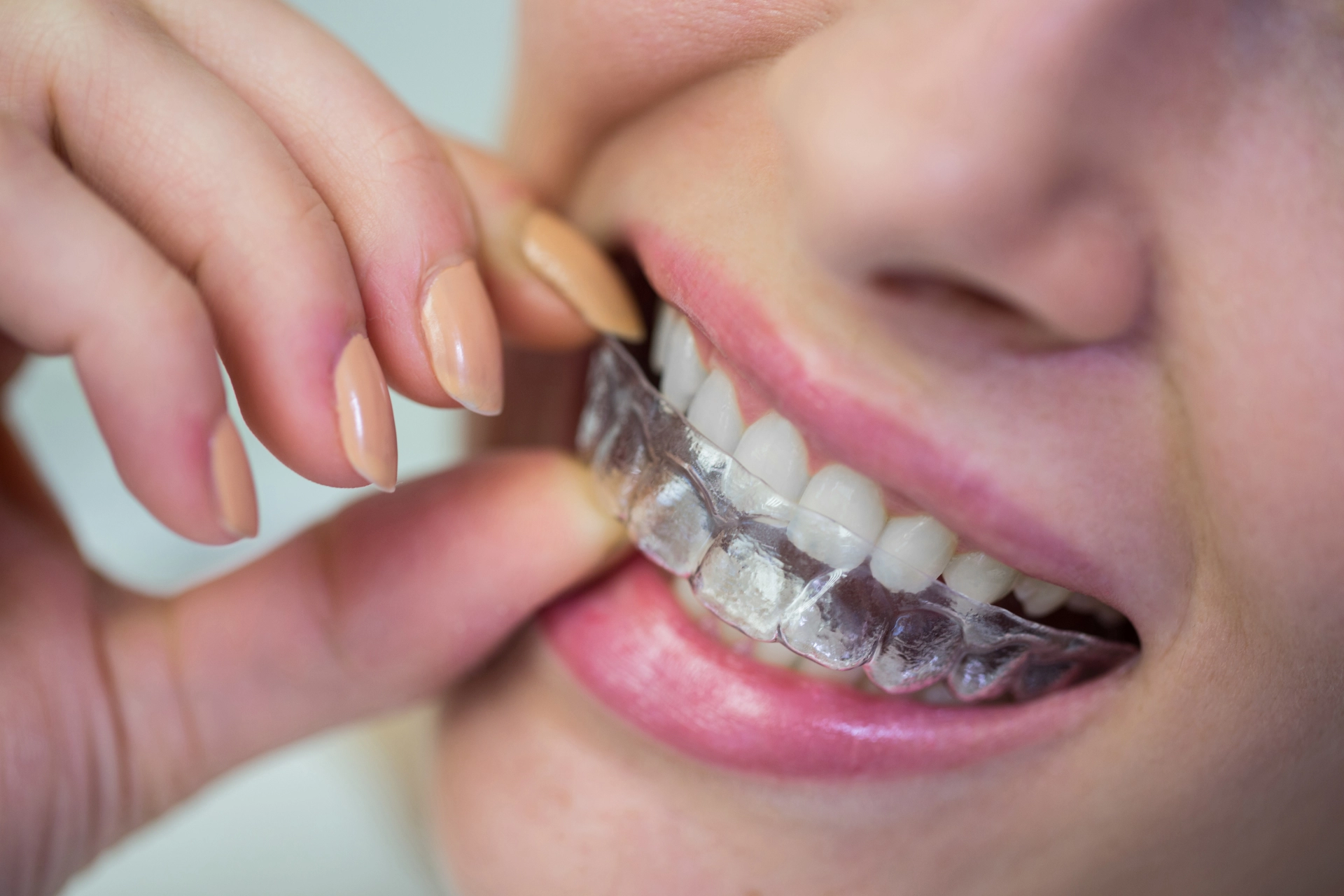
What is bite correction?
02 February 2026
Bite correction is a dental and orthodontic treatment focused on improving how the upper and lower teeth fit together, a relationship known as occlusion. When the bite is properly aligned, the teeth, jaw muscles, and joints work together smoothly. When it is not, everyday actions such as chewing, speaking, or swallowing can become uncomfortable and inefficient.Many people believe orthodontic treatment is only about straight teeth, but bite alignment is just as important. A healthy bite protects your teeth from damage, supports jaw function, and contributes to overall oral and facial health.Understanding Bite Problems (Malocclusion)A misaligned bite, also called malocclusion, occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not align correctly when the mouth is closed. This condition may be caused by genetics, jaw development issues, missing teeth, injuries, or childhood habits.Common bite problems include:1. Overbite, Underbite, and CrossbiteAn overbite occurs when the upper teeth excessively overlap the lower teeth, while an underbite happens when the lower teeth extend past the upper teeth. A crossbite occurs when upper teeth sit inside the lower teeth instead of outside.2. Open Bite and CrowdingAn open bite means the teeth do not touch when biting down. Crowded or crooked teeth can also prevent proper alignment and lead to uneven pressure on teeth.3. General MisalignmentImproper spacing or positioning of teeth can affect chewing efficiency, oral hygiene, and jaw comfort.If left untreated, malocclusion may cause jaw pain, headaches, worn or damaged teeth, gum disease, and changes in facial appearance.Functional Benefits of Bite CorrectionBite correction improves how your mouth functions and helps prevent long-term oral problems.• Better chewing and clearer speechAligned teeth make eating more comfortable and can reduce speech difficulties.• Jaw pain and TMJ reliefCorrecting bite alignment reduces strain on jaw muscles and joints, easing tension, clicking, and discomfort.• Protection from tooth damageEvenly distributed bite pressure helps prevent enamel wear, chipping, and cracking.Proper alignment also makes brushing and flossing easier, lowering the risk of cavities and gum disease.Aesthetic and Confidence BenefitsBite correction doesn’t just improve function—it also enhances appearance. Proper alignment creates a more balanced smile, improves facial symmetry, and reduces crowding or gaps. Over time, untreated bite problems may contribute to premature facial aging or jawline changes.A healthy, aligned smile often leads to increased confidence, positively affecting both personal and professional life.Causes and Symptoms of a Bad BiteMalocclusion is often inherited, but it can also result from habits or medical conditions. Common causes include: thumb-sucking, prolonged pacifier use, jaw injuries, missing or impacted teeth, teeth grinding, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, and poor oral hygiene. Symptoms may include: difficulty chewing, jaw pain or clicking, headaches, speech issues, frequent cheek or tongue biting, mouth breathing, and noticeable changes in facial appearance.Bite Correction Treatment OptionsTreatment depends on the severity of the problem and the patient’s age.1. Orthodontic TreatmentsTraditional braces and clear aligners gradually move teeth into proper alignment and are effective for mild to complex cases.2. Restorative ProceduresCrowns, bridges, implants, or tooth replacement can help restore bite balance when teeth are missing or damaged.3. Advanced or Supportive TreatmentsBite adjustment, jaw expanders, headgear, tooth extraction, or jaw surgery may be recommended in more severe cases.Treatment typically lasts between 12 months and two and a half years, with regular checkups to monitor progress.When Is Bite Correction Necessary?Not every mild bite issue requires treatment. However, if malocclusion affects eating, speaking, breathing, oral hygiene, or causes pain or tooth damage, professional care is important. Early treatment—especially in children—is often easier, but adults can benefit from bite correction at any age.Take the First Step Toward a Healthier SmileA misaligned bite can affect your comfort, confidence, and long-term oral health. Early diagnosis and timely treatment help prevent complications and improve quality of life.If you are concerned about your bite, the experienced dental team at Dalimed Medical Center is ready to help. We provide personalized bite correction solutions using modern techniques to restore function and enhance your smile. Don’t wait—schedule a consultation at Dalimed Medical Center and take an important step toward a healthier, more confident future.